The modern era of aerospace exploration is undergoing a seismic shift. With the evolution of robotics and AI technology, our capacity to achieve groundbreaking feats in space exploration has dramatically expanded. One of the most compelling advancements in recent times has been the development of Robotic Space Assembly Inspired by Human Arm Dynamics.
Understanding Human Arm Dynamics
Human arm dynamics are a marvel of biological engineering. The synergy of our bones, muscles, tendons, and neural pathways allows us to perform intricate tasks with precision. By understanding the principles of these dynamics, we can replicate them in robotic mechanisms.
- Leverage and Force Distribution: Just as our forearm acts as a lever, providing balance and strength in our motions, robotic arms are designed to efficiently distribute force across their structure.
- Flexibility and Range of Motion: Our shoulder joint offers an impressive range of motion. Translating this flexibility to robotic arms ensures they can reach, pivot, and rotate in various orientations.
- Tactile Feedback and Sensitivity: Our fingertips are equipped with an array of sensors, providing rich feedback. Modern robotics integrates similar sensors to detect changes in environment and adjust movements accordingly.
Applying Human Arm Dynamics to Robotic Space Assembly
The space environment is fraught with challenges – extreme temperatures, vacuum, and microgravity conditions. Thus, conventional assembly techniques fall short. Leveraging human arm dynamics can make a significant difference.
Precision Assembly in Microgravity
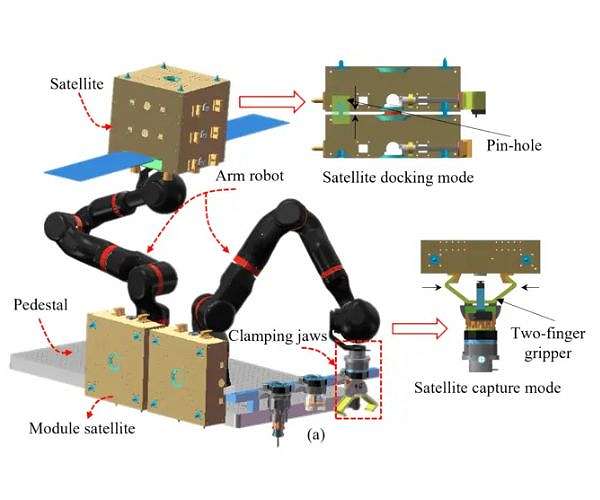
Microgravity poses challenges for assembly tasks. But by imitating the human arm’s balance and force distribution mechanisms, robotic arms can maneuver components with unparalleled precision.
Thermal Protection and Resistance
Drawing inspiration from our body’s ability to regulate temperature, robotic mechanisms are designed with materials and structures that resist extreme thermal variations, ensuring longevity and functionality.
Efficient Power Utilization
Our muscles are incredibly energy-efficient. Similarly, these robotic systems are optimized for minimal power consumption, ensuring they operate for extended periods without depleting energy resources.
The Pioneers Behind the Revolution
Several defense and aerospace industry specialists have been instrumental in this transformative journey.
Acme Aerospace: With their state-of-the-art R&D facility, Acme Aerospace has been at the forefront, developing robotic arms that can autonomously assemble space structures. Their patented ‘Bio-Dynamic Assembly System’ has been a game-changer.
Orion Robotics: Orion’s ‘Tactile Precision System’ integrates advanced sensors, mirroring the human fingertip’s sensitivity. This has revolutionized how robotic arms perceive and interact with their surroundings in space.
Advent of Modular Space Structures
One of the most significant applications of these robotic assembly techniques has been in the construction of modular space structures. Whether it’s building vast solar arrays or assembling space habitats, these robots have made it feasible.
Challenges and Future Prospects
While the integration of human arm dynamics into space robotics has been revolutionary, challenges persist. Micro-meteoroids and space debris pose threats. Moreover, long-term operations require solutions for wear and tear.
However, with continuous R&D and advancements in materials science, the future looks promising. The next decade could very well see the establishment of large-scale space structures, assembled entirely by robots inspired by the marvel of human arm dynamics.
Concluding Remarks
In sum, the blend of biology and technology has paved the way for some of the most exciting advancements in aerospace. The future of space exploration and habitation is brighter than ever, thanks to the groundbreaking methods of robotic space assembly inspired by human arm dynamics.