In the complex landscape of global security and international relations, crisis management stands as a pivotal pillar for organizations like NATO. However, recent research suggests that the concept of crisis management within NATO has been treated somewhat ambiguously, prompting a call for increased clarity in its approach. In this article, we delve into the insights provided by researchers who advocate for a more defined crisis management strategy within NATO.
NATO’s Crisis Management Strategy: A Closer Look
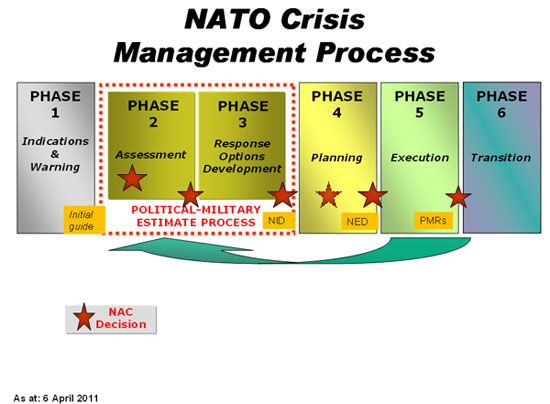
NATO, the North Atlantic Treaty Organization, is a collective defence alliance that plays a critical role in maintaining stability and security among its member states. One of the key components of NATO’s mission is crisis management – the ability to effectively respond to unforeseen events and emergent threats. Such events could range from military confrontations to humanitarian crises or cyberattacks.
While NATO has historically demonstrated its capability to address crises, some researchers argue that there exists a degree of ambiguity in how the alliance approaches crisis management. This ambiguity can lead to inefficiencies and challenges when responding to rapidly evolving situations.
Researchers Push for Clarity
In a recent study conducted by a team of researchers specializing in international security and crisis management, attention was drawn to the concept of crisis management within NATO. The study examined historical cases and crisis scenarios to identify patterns and gaps in NATO’s approach.
The researchers highlighted the importance of clearly defined protocols, communication strategies, and decision-making processes. They stressed that ambiguity in these areas could hinder the alliance’s ability to respond effectively to crises. Additionally, the researchers identified the need for continuous training and preparedness exercises to ensure that NATO’s crisis management teams are ready to tackle any challenge.
Recommendations for an Enhanced Approach
Based on their analysis, the researchers put forth several recommendations aimed at enhancing NATO’s crisis management approach:
- Clear Communication: NATO should establish unambiguous communication channels to ensure that information flows seamlessly among member states, enabling swift and coordinated responses.
- Structured Decision-Making: The alliance should adopt a structured decision-making framework that outlines the roles, responsibilities, and decision pathways of various stakeholders during a crisis.
- Scenario-Based Training: Regular training exercises should be conducted, simulating diverse crisis scenarios to prepare personnel for a wide range of potential challenges.
- Public Diplomacy: Transparency and public communication during crises can help maintain public confidence and international cooperation. NATO should develop effective strategies for conveying accurate information to the public and the media.
FAQs about NATO’s Crisis Management:
Q1: What is NATO’s primary mission? A1: NATO’s primary mission is to ensure the security and defence of its member states through collective defence measures.
Q2: What is crisis management within NATO? A2: Crisis management within NATO involves the alliance’s ability to respond effectively to unexpected events and emergent threats, ranging from military conflicts to humanitarian crises.
Q3: Why is clarity important in NATO’s crisis management? A3: Clarity is crucial in crisis management to ensure well-defined protocols, streamlined decision-making, and effective communication, enabling prompt and coordinated responses.
Q4: How can NATO enhance its crisis management approach? A4: NATO can enhance its crisis management by establishing clear communication channels, adopting structured decision-making frameworks, conducting scenario-based training, and practising transparent public diplomacy.
Q5: What role does research play in shaping NATO’s strategies? A5: Research provides valuable insights and recommendations that can guide NATO in refining its strategies, improving its effectiveness, and adapting to evolving security challenges.